Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shiro, Ayumi*; Shobu, Takahisa; Hagihara, Koji*; Watanabe, Masashi*
SPring-8/SACLA Riyo Kenkyu Seikashu (Internet), 10(5), p.438 - 446, 2022/10
no abstracts in English
Shobu, Takahisa; Shiro, Ayumi*; Kono, Fumiaki*; Muramatsu, Toshiharu; Yamada, Tomonori; Naganuma, Masayuki; Ozawa, Takayuki
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 5(2), p.17_1 - 17_9, 2021/06
The automotive industries employ laser beam welding because it realizes a high energy density without generating irradiation marks on the opposite side of the irradiated surface. Typical measurement techniques such as strain gauges and tube X-rays cannot assess the localized strain at a joint weld. Herein high-energy synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction was used to study the internal strain distribution of laser lap joint PNC-FMS steels (2- and 5-mm thick) under loading at a high temperature. As the tensile load increased, the local tensile and compressive strains increased near the interface. These changes agreed well with the finite element analysis results. However, it is essential to complementarily utilize internal defect observations by X-ray transmission imaging because the results depend on the defects generated by laser processing.
Shibayama, Yuki; Hojo, Tomohiko*; Koyama, Motomichi*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Yasuda, Ryo*; Shobu, Takahisa; Matsuno, Takashi*; Akiyama, Eiji*
ISIJ International, 61(4), p.1322 - 1329, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.78(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Morooka, Satoshi
Hozengaku, 19(1), p.29 - 34, 2020/04
no abstracts in English
Bae, J. W.*; Jung, J.*; Kim, J. G.*; Park, J. M.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Woo, W.*; Kim, H. S.*
Materialia, 9, p.100619_1 - 100619_15, 2020/03
Shimada, Koji
Chishitsu Gijutsu, (9), p.25 - 40, 2019/09
Today many collaborations are there in Earth-scientific research and development. Structural geology can serve crucial information on tectonic strain at sampling point in Japan, belonging to the circum-Pacific orogenic belt. Visualize of strain estimation would be effective during field geological survey and for better understanding for non-specialist on structural geology. Illustrations decoding mathematical expressions of strain estimation methods are presented here.
Kasahara, Shigeki; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Hata, Kuniki; Hanawa, Satoshi
Zairyo To Kankyo, 68(9), p.240 - 247, 2019/09
In order to study environment assisted cracking mechanism of stainless steel under BWR primary coolant condition, effects of applied load on oxidation in the vicinity of crack tips of CT specimens were evaluated. Loaded CT specimens were immersed in an aqueous condition at 290 C as a simulated BWR coolant condition, and microstructural observation on oxide near the tips of pre-cracks was carried out. Oxide inner layers, which consisted of fine grain magnetite containing Fe and Cr were formed, and oxide outer layers consisting of large grains of Fe
C as a simulated BWR coolant condition, and microstructural observation on oxide near the tips of pre-cracks was carried out. Oxide inner layers, which consisted of fine grain magnetite containing Fe and Cr were formed, and oxide outer layers consisting of large grains of Fe O
O were observed to cover the inner layers. FEM analysis of stress and strain in the loaded CT specimen suggests that both of dislocations due to localized plastic deformation and elastic strain could play important roles to accelerate inner oxide formation in the vicinity of the crack tip of the specimens.
were observed to cover the inner layers. FEM analysis of stress and strain in the loaded CT specimen suggests that both of dislocations due to localized plastic deformation and elastic strain could play important roles to accelerate inner oxide formation in the vicinity of the crack tip of the specimens.
Ebihara, Kenichi; Saito, Kei*; Takai, Kenichi*
"Suiso Zeika No Kihon Yoin To Tokusei Hyoka" Kenkyukai Hokokusho, p.57 - 61, 2018/09
no abstracts in English
Morooka, Satoshi; Suzuki, Hiroshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 60(5), p.289 - 293, 2018/05
, 60(5), p.289 - 293, 2018/05
no abstracts in English
Akita, Koichi; Nakatani, Hayato*; Ogihara, Shinji*; Shobu, Takahisa; Shiro, Ayumi*; Igawa, Naoki; Shimojo, Yutaka
SPring-8/SACLA Riyo Kenkyu Seikashu (Internet), 6(1), p.105 - 108, 2018/01
no abstracts in English
Okajima, Satoshi; Wakai, Takashi
Nihon Kikai Gakkai 2017-Nendo Nenji Taikai Koen Rombunshu (DVD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2017/09
It was reported that the long distance travel of temperature distribution causes a new type of thermal ratcheting, even in the absence of primary stress. In this paper, based on the results of inelastic finite element analyses, we investigated saturation behavior of thermal ratcheting strain due to long range travel of temperature distribution. As a result, we revealed that the long distance travel of temperature distribution generates plastic strain distribution made maximum at the central part. Because of the shape of the generated strain distribution, the residual stress accumulates even at the central part of the region passed through the temperature distribution. In the case with excessive long traveling of temperature distribution, the region with plastic deformation extended to the surrounding region. Otherwise, sufficient magnitude of residual stress to cause shakedown behavior accumulated on entire region, and the accumulation of the plastic strain saturated.
Tsuchida, Noriyuki*; Nagahisa, N.*; Harjo, S.
Materials Science & Engineering A, 700, p.631 - 636, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:38.56(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) Sn strands of CIC conductor using neutron diffraction
Sn strands of CIC conductor using neutron diffractionHemmi, Tsutomu*; Harjo, S.; Kajitani, Hideki*; Suwa, Tomone*; Saito, Toru*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Osamura, Kozo*; Koizumi, Norikiyo*
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 27(4), p.4200905_1 - 4200905_5, 2017/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.94(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Ojima, Mayumi*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Inoue, Junya*; Shobu, Takahisa; Xu, P. G.; Akita, Koichi; Nambu, Shoichi*; Koseki, Toshihiko*
Zairyo, 66(6), p.420 - 426, 2017/06
Ikeda, Yoshimasa*; Taketani, Atsushi*; Takamura, Masato*; Sunaga, Hideyuki*; Kumagai, Masayoshi*; Oba, Yojiro*; Otake, Yoshie*; Suzuki, Hiroshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 833, p.61 - 67, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:96.62(Instruments & Instrumentation)A compact accelerator-based neutron source has been lately discussed on engineering applications such as transmission imaging and small angle scattering as well as reflectometry. However, nobody considers using it for neutron diffraction experiment because of its low neutron flux. In this study, therefore, the neutron diffraction experiments are carried out using Riken Accelerator-driven Compact Neutron Source (RANS), to clarify the capability of the compact neutron source for neutron engineering diffraction. The diffraction pattern from a ferritic steel was successfully measured by suitable arrangement of the optical system to reduce the background noise, and it was confirmed that the recognizable diffraction pattern can be measured by the large sampling volume with 10 mm in cubic for an acceptable measurement time, i.e. 10 minutes. The minimum resolution of the 110 reflection for RANS is approximately 2.5 % at 8  s of the proton pulse width, which is insufficient to perform the strain measurement by neutron diffraction. The moderation time width at the wavelength corresponding to the 110 reflection is estimated to be approximately 30
s of the proton pulse width, which is insufficient to perform the strain measurement by neutron diffraction. The moderation time width at the wavelength corresponding to the 110 reflection is estimated to be approximately 30  s, which is the most dominant factor to determine the resolution. Therefore, refinements of the moderator system to decrease the moderation time are important to improve the resolution of the diffraction experiment using the compact neutron source. In contrast, the texture evolution due to plastic deformation was successfully observed by measuring a change in the diffraction peak intensity by RANS. Furthermore, the volume fraction of the austenite phase was also successfully evaluated by fitting the diffraction pattern using a Rietveld code. Consequently, RANS was proved to be capable for neutron engineering diffraction aiming for the easy access measurement of the texture and the amount of retained austenite.
s, which is the most dominant factor to determine the resolution. Therefore, refinements of the moderator system to decrease the moderation time are important to improve the resolution of the diffraction experiment using the compact neutron source. In contrast, the texture evolution due to plastic deformation was successfully observed by measuring a change in the diffraction peak intensity by RANS. Furthermore, the volume fraction of the austenite phase was also successfully evaluated by fitting the diffraction pattern using a Rietveld code. Consequently, RANS was proved to be capable for neutron engineering diffraction aiming for the easy access measurement of the texture and the amount of retained austenite.
Naoe, Takashi; Xiong, Z.; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 468, p.331 - 338, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:85.7(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Mercury enclosure vessel of the JSNS made of an austenitic stainless steel suffers radiation damage in the proton and neutron environment. In addition to the radiation damage, the vessel suffers the cyclic impact loading caused from the pressure waves. The JSNS target vessel suffers higher than 2 10
10 cyclic loading. Furthermore, strain rate of the beam window portion of the target vessel reaches to 50s
cyclic loading. Furthermore, strain rate of the beam window portion of the target vessel reaches to 50s at the maximum, which is much higher than the conventional fatigues. Very high cycle fatigue strengths up to 10
at the maximum, which is much higher than the conventional fatigues. Very high cycle fatigue strengths up to 10 cycles for solution annealed (SA) and 10% cold-worked 316L (CW) were investigated through the ultrasonic fatigue test. The result showed that the fatigue strengths of SA and CW tested in high-strain rate were higher than that of the conventional fatigue. On the other hand, the fatigue failure occurred regardless of material and temperature in the very high-cycle region (
cycles for solution annealed (SA) and 10% cold-worked 316L (CW) were investigated through the ultrasonic fatigue test. The result showed that the fatigue strengths of SA and CW tested in high-strain rate were higher than that of the conventional fatigue. On the other hand, the fatigue failure occurred regardless of material and temperature in the very high-cycle region (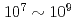 cycles) at the stress amplitude of below the conventional fatigue limit.
cycles) at the stress amplitude of below the conventional fatigue limit.
Ishijima, Yasuhiro; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2015/05
In this study, to evaluate the effect of thermal aging on creep properties of Alloy 625, we carried out creep tests on aged and solution-treated Alloy 625 at 1073 K. According to the creep test results, time-to-rupture decreased by thermal aging when test stress was more than 100 MPa, but did not change when test stress was less than 100 MPa for any specimens. In the solution-treated alloy, creep deformation behaviors changed over 100 MPa. These results show that time-to-rupture was constant because intermetallic compounds precipitated when the test stress was less than 100 MPa in solution-treated alloy. The observed relationship between creep strain rate and test time showed that the precipitation started after 100 hr for solution treated alloys. These results suggest that intermetallic compounds precipitate immediately after furnace operation. And it is appropriate to use creep data of thermal-aged Alloy 625 for the reducing roasting furnace lifetime prediction.
Nishi, Hiroshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(1-7), p.269 - 274, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.68(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tensile strength of the diffusion bonded joint was as large as that of Alumina dispersion-strengthened copper (DS Cu), however, the Charpy absorbed energy of the joint was considerably lower than that of DS Cu. Instrumented Charpy impact test and slow-bend Charpy test of diffusion bonded joints were performed to clarify the degradation of Charpy absorbed energy. Elasto-plastic analyses were also carried out in order to study the deformation behavior of the tensile and V-notched specimens for joints. As the results, the fracture behaviors of the impact and slow-bend tests were almost the same. Elasto-plastic analyses showed that the maximum strain occurred at the DS Cu apart from the interface for tensile specimen, however, the strain concentrated at the DS Cu near the interface for the notched specimen. This strain concentration arose from the mechanical heterogeneity between stainless steel and DS Cu in the bonded zone and attributed to the degradation of the absorbed energy of the joints.
Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Tsukada, Takashi
Nihon Kikai Gakkai M&M 2005 Zairyo Rikigaku Kanfarensu Koen Rombunshu, p.175 - 176, 2005/12
From results of analysis of plastic deformation behavior at SCC crack tip by EBSP method, the conclusions was obtained as follows: (1)Regarding to basic data for quantitative evaluation of plastic deformation behavior at SCC crack tip, we obtained relationship between plastic deformation and misorientation of grain using SSRT result for SUS316L stainless steel in high temperature water and local plastic strain was able to estimate using this relationship. (2)From experimental results of plastic strain at SCC crack and ductile crack tips using relationship between misorientation and plastic deformation, plastic strain near ductile crack tip was larger than that at SCC crack tip. Plastic deformation region was, however, corresponded to region of about one grain at crack tip for both SCC and ductile cracks.
Igarashi, Shinichi*; Itakura, Akiko*; Kitajima, Masahiro*; Nakano, Shinsuke*; Muto, Shunsuke*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Hojo, Kiichi
Hyomen Kagaku, 25(9), p.562 - 567, 2004/09
Surface stress can be utilized positively in modifying the surface reaction potential and increasing the surface reactivity. Blister is a local protrusion of solid surface induced by gas ion irradiation, and is considered to create local stress on surface layers. Si(100) substrate was irradiated with 10 keV H (fluence; 1
(fluence; 1 10
10 ions/m
ions/m ) at an angle of 30
) at an angle of 30 to the surface normal. The blisters of several
to the surface normal. The blisters of several  m in diameter at the bottom were formed. After the ion irradiation, the substrate was oxidized. By means of scanning Auger microscopy, we observed that the rims of the blisters have higher oxygen intensities than the flat surfaces and the tops have lower than the flats. The calculated stress distribution of the blister shows that the surface layers should be stretched laterally at the top of blisters and are compressed at the rim, relative to the flat surfaces. The O distribution clearly consists with the stress distribution of the surface. Our results demonstrate a patterned oxidation of Si surface applying its reactivity depending on the surface stress.
m in diameter at the bottom were formed. After the ion irradiation, the substrate was oxidized. By means of scanning Auger microscopy, we observed that the rims of the blisters have higher oxygen intensities than the flat surfaces and the tops have lower than the flats. The calculated stress distribution of the blister shows that the surface layers should be stretched laterally at the top of blisters and are compressed at the rim, relative to the flat surfaces. The O distribution clearly consists with the stress distribution of the surface. Our results demonstrate a patterned oxidation of Si surface applying its reactivity depending on the surface stress.